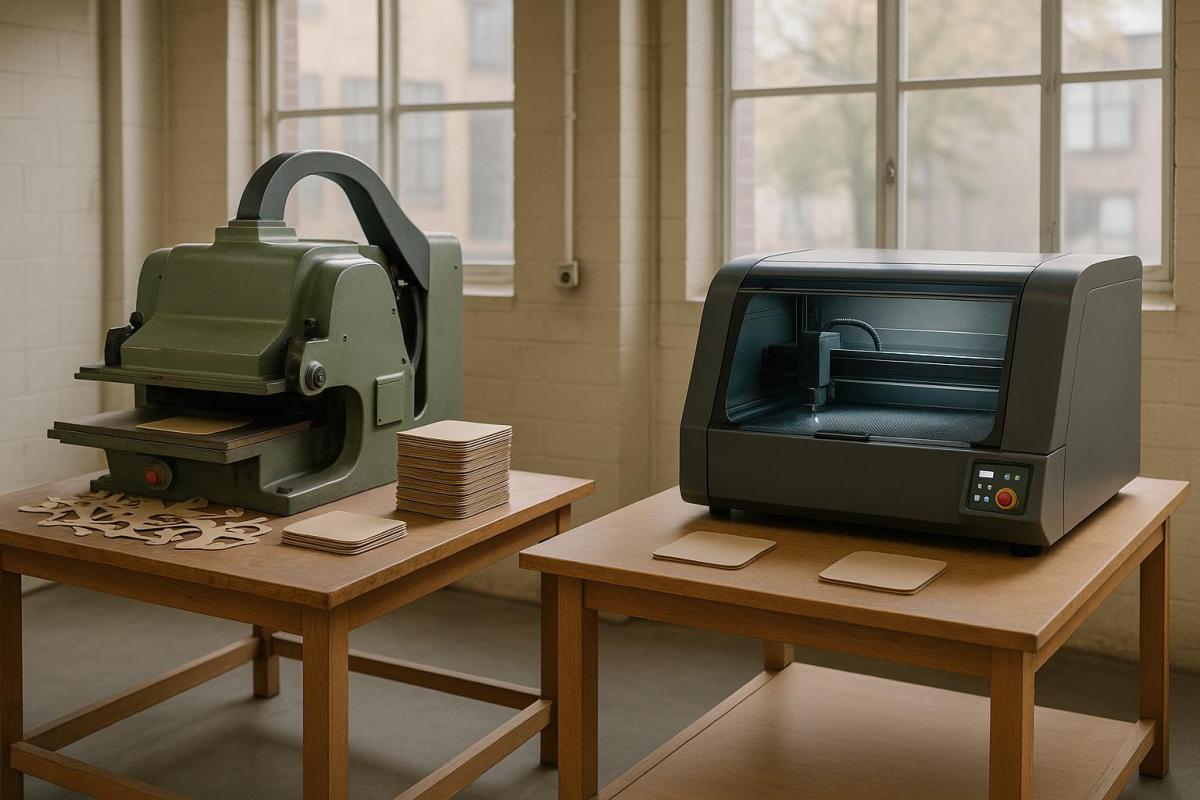
Laser cutting is more energy-efficient and produces less waste than die cutting, making it a better choice for sustainability-focused projects. Here’s a quick breakdown of the two methods:
- Energy Use: Laser cutting uses less energy, especially with modern fiber lasers, while die cutting relies on large, energy-intensive machines.
- Waste Production: Laser cutting generates minimal waste due to its precision, whereas die cutting produces more scrap and requires physical dies that eventually need disposal.
- Material Efficiency: Laser cutting excels at intricate designs and prototypes, while die cutting is better for high-volume, simple shapes.
Quick Comparison
| Factor | Die Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | High, due to large machines and maintenance | Lower, especially with fiber lasers |
| Waste Production | More waste from scraps and die disposal | Minimal waste due to precision cutting |
| Material Efficiency | Good for simple, high-volume projects | Excellent for detailed designs and prototypes |
Laser cutting is ideal for precision and sustainability, while die cutting works well for large-scale, straightforward jobs. Choose based on your project’s needs!
Xymox – Die Cut vs Laser
Die Cutting Process and Eco Impact
Die cutting involves shaping materials using custom steel dies and presses. To understand its environmental impact, it’s essential to examine energy consumption, waste generation, and material efficiency.
Energy Consumption in Die Cutting
Die cutting relies heavily on mechanical presses and steel dies, which require significant energy during both the cutting process and the production and maintenance of the dies themselves.
In fact, machine tool electricity accounts for 75% of manufacturing energy use and 90% of industrial energy consumption. This highlights the importance of optimizing machine settings and material choices to enhance efficiency. For instance, a packaging company improved its sustainability efforts by switching from traditional cardboard to recycled composite materials. By adjusting their die cutting machine settings to accommodate the new material, they achieved cleaner cuts and reduced energy use.
Energy consumption directly ties into waste production, which is the next critical area to consider.
Waste Production in Die Cutting
The die cutting process generates waste primarily in the form of leftover material surrounding cutouts, scraps, and damaged pieces caused by poorly maintained dies. Additionally, the disposal of steel dies after their lifecycle contributes to waste.
However, innovative recycling solutions are emerging to tackle these issues. In 2021, Batavia Container Inc., in collaboration with Mid America Paper Recycling, recycled outdated dieboards into products like lawn mulch and other wood-based items. A specialized chipper separated the metal components from the wood, making repurposing possible.
"Preventing old cutting dies from ending up in a landfill will help all of us." – Paul Mansour, Director of Account Development at Batavia Container
"The boards were sent through a high-tech wood chipper that can separate the metal tool from the wood. The resulting wood chips can be reused as mulch and other wood-based products." – Paul Pirkle, President of Mid America Paper Recycling
Precision engineering and advanced nesting techniques also help reduce waste. CAD software can simulate the die cutting process, highlighting areas for improvement, while nesting algorithms optimize the placement of cutouts to use materials more efficiently. Automated waste removal systems further enhance production quality by preventing tool damage and minimizing material defects. These measures underscore the need for thoughtful material usage to boost sustainability.
Material Usage in Die Cutting
One of die cutting’s strengths lies in its ability to maximize material efficiency. By utilizing the full width and length of materials, this process reduces waste and increases the number of parts produced per roll. This precision is especially beneficial when working with costly materials, as minimizing waste directly lowers expenses.
Digital die cutting offers another advantage, particularly for prototypes and small-scale projects. It allows businesses to test and refine designs before committing to large production runs, reducing material waste in the process. However, traditional steel dies, once manufactured, cannot be easily modified. This limitation can result in less efficient material use if design changes become necessary.
The rapid growth of e-commerce has further emphasized the importance of efficient material use. The global e-commerce packaging market was valued at $63.6 billion in 2022, with annual growth rates of 20% between 2017 and 2021. As this market expands, the environmental impact of packaging production grows, making material efficiency a key concern.
Automation plays a significant role in addressing these challenges. By streamlining production and reducing waste, automated systems lower both costs and environmental footprints.
Laser Cutting Process and Eco Impact
Laser cutting relies on concentrated light beams to cut materials with precision. Unlike the mechanical method of die cutting, this digital approach has unique environmental implications, particularly in energy use, waste production, and material efficiency.
Energy Consumption in Laser Cutting
The energy used by laser cutting machines varies widely, ranging from 0.1 kW to 15 kW, depending on machine type and workload. The laser technology in use plays a major role in energy efficiency. For example, fiber lasers are far more efficient than CO₂ lasers. A 1 kW fiber laser typically requires 1.5–2 kW of total power, whereas a comparable CO₂ laser needs 3–4 kW. The gap widens with high-power systems, where CO₂ lasers can consume around 70 kW compared to just 18 kW for fiber lasers.
Factors like material thickness, reflectivity, and environmental conditions – such as temperature and humidity – also influence energy demands. To combat energy waste, some machines integrate advanced fiber laser resonators, lightweight gantries, and automated power controls. Features like nesting power output control help adjust laser intensity based on the material, further improving efficiency.
These advancements not only cut energy costs but also reduce waste during the cutting process.
Waste Production in Laser Cutting
Thanks to its precision, laser cutting generates less waste compared to traditional cutting methods. Most waste comes in the form of off-cuts, scrap, and dross, but digital control significantly limits these byproducts. Fiber laser cutting, for instance, can reduce material waste by 15–30%, with stainless steel seeing improvements up to 35%, aluminum around 25%, and carbon steel between 20–30%.
Real-world examples highlight this efficiency. Ashley Furniture Industries slashed sheet-cutting waste by 75% after adopting CNC cutting and implementing practices to sell or donate scrap materials. Similarly, Signarama reduced sheet-cutting waste by 90% by switching to waterjet cutting and refining scrap management.
Nesting software also plays a key role in waste reduction. By optimizing material placement and cutting paths, it can decrease waste by as much as 25%. Unlike die cutting, laser cutting eliminates the need for physical dies, avoiding the waste associated with their creation, maintenance, and disposal.
Material Usage in Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is highly efficient in material usage, offering a level of precision that sets it apart from die cutting. With accuracy up to ±0.1 mm and kerf widths as narrow as 0.1 mm, laser cutting maximizes material utilization. In fact, sheet utilization rates can reach up to 94%. For example, DOMUSA Teknik replaced mechanical steel cutters with fiber laser systems for boiler production, achieving a 94.1% sheet utilization rate and lowering both waste and costs.
This technology also reduces material loss caused by wide cutting tools, minimizing rework. With digital file-based designs and advanced nesting software, manufacturers can optimize material use in real time, ensuring every sheet is used as efficiently as possible.
Neway Precision Works Ltd. highlights: "Laser-cutting technology is pivotal in sustainable manufacturing because it reduces waste and improves production efficiency… laser cutting helps manufacturers optimize material usage while maintaining high-quality production standards."
TAB Industries adds: "Efficiency and sustainability are inherent in laser cutting, thanks to advanced nesting software. This technology optimizes material utilization by strategically arranging parts on a single sheet, minimizing scrap and maximizing cost-effectiveness."
Additionally, the process involves minimal use of chemicals and solvents, further reducing its overall environmental footprint.
sbb-itb-ce53437
Side-by-Side Comparison: Die Cutting vs Laser Cutting
When evaluating die cutting and laser cutting from an environmental perspective, three main factors stand out: energy consumption, waste generation, and material efficiency. Both methods have their strengths, and the right choice often depends on the specifics of the project, including production volume and design complexity.
Energy Consumption
Die cutting relies on large machines and dies that consume a lot of energy. These machines also require frequent maintenance, which contributes to higher carbon emissions. On the other hand, laser cutting uses a focused light beam, which operates with fewer consumables and requires less maintenance. Its speed and efficiency help reduce the overall energy footprint.
Waste Generation
Die cutting tends to produce more waste due to the material trimming involved in the process. Laser cutting, however, is highly precise, targeting only the necessary material. This precision not only reduces waste but also makes recycling easier.
Material Efficiency
Die cutting performs well for high-volume projects with simple shapes. Laser cutting, by contrast, is ideal for intricate designs and prototypes. However, minor material losses can occur with laser ablation, particularly for complex designs.
These differences are evident in real-world applications. For instance, in the aerospace industry, laser cutting is used to create lightweight, durable parts with minimal waste, helping to lower costs and environmental impact. Similarly, in the automotive sector, laser technology enables the production of high-precision components that improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Comparison Table
| Environmental Factor | Die Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | High energy use from large machines; frequent maintenance adds to emissions | Lower energy usage with faster operation and minimal maintenance |
| Waste Generation | Significant waste due to material trimming | Minimal waste thanks to precise cutting; scrap is often recyclable |
| Material Efficiency | Best for high-volume, simple shapes | Excellent for intricate designs and prototypes; minor losses from laser ablation |
| Best Applications | High-volume runs of basic shapes | Low-volume custom work, prototypes, and detailed designs |
| Maintenance Impact | Frequent tool and die replacement increases environmental footprint | Few consumables required; equipment longevity reduces maintenance needs |
Ultimately, choosing between die cutting and laser cutting depends on your production requirements. Die cutting may be the better option for large-scale projects with straightforward designs, while laser cutting stands out for its precision, waste reduction, and energy efficiency in smaller, more complex jobs.
To further reduce environmental impact, manufacturers can take steps such as using energy-efficient equipment, fine-tuning cutting parameters, or integrating renewable energy sources into their processes. The laser cutting market, projected to grow to $14.52 billion by 2026, reflects the rising demand for these sustainable technologies.
Eco-Friendly Practices at Miro Printing & Graphics Inc.
At Miro Printing & Graphics Inc., based in Hackensack, NJ, environmental responsibility is at the core of their die cutting and laser cutting operations. By focusing on energy efficiency, waste reduction, and material optimization, the company integrates sustainable practices into every aspect of its facility while maintaining top-tier printing and post-press services.
Digital Technology for Reducing Waste
Miro employs digital die cutting technology to help cut down on waste, making it particularly effective for prototypes and short-run projects. This approach minimizes material use and ensures precision in every cut.
Their laser cutting services also play a big role in minimizing waste. Unlike traditional methods, laser cutting eliminates the need for physical dies and allows for intricate shapes and designs without overcuts or excess scrap. This level of accuracy not only saves material but also reduces costs, offering both environmental and financial benefits.
Efficient Use of Materials
Material efficiency is a key focus of Miro’s die cutting services. By using engineered dies, they achieve precise cuts and creases tailored to a product’s dimensions. This customization enhances product protection while cutting down on unnecessary material use.
Laser cutting further enhances efficiency. Its precision means less raw material is needed to produce the same volume of products. Additionally, Miro incorporates energy-saving technologies into their processes, ensuring that every step supports their sustainability goals.
Energy-Conscious Operations
Miro prioritizes eco-friendly printing methods that use less energy without compromising quality. Their digital cutting services are a prime example, offering a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional printing techniques. This approach aligns with their broader commitment to reducing their environmental footprint while delivering excellent results.
Sourcing Sustainable Materials
The company also promotes the use of sustainable materials. By collaborating with clients, Miro helps select eco-friendly options such as recycled acrylics and other recycled materials. This effort meets the growing demand for greener printing solutions in the Bergen County area.
Innovative Processes
Miro’s laser cutting technology employs an advanced ablation process, where a focused laser beam removes material through sublimation. This technique allows for clean, precise cuts with minimal waste, outperforming traditional mechanical cutting methods in terms of both efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion
Laser cutting stands out for its clear environmental benefits compared to die cutting. By offering precision that reduces material waste by 30–60%, laser cutting minimizes the scrap often associated with methods like sawing or punching. Its narrow kerf widths and focused beam technology are key contributors to this efficiency.
While die cutting remains suitable for certain applications, it typically results in higher waste and carbon emissions. Both methods, however, can benefit from using recycled materials, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient machinery.
As Stephens Gaskets highlights:
"Laser cutting has proven to be a powerful tool in supporting sustainable manufacturing. By reducing material waste, conserving energy, and lowering carbon emissions, laser technology enables businesses to achieve their environmental goals without compromising on quality or precision."
- Stephens Gaskets
The importance of sustainability is also reflected in consumer behavior. According to recent data, 78% of consumers prioritize sustainable lifestyle choices, with many willing to pay up to 28% more for eco-friendly products. This trend underscores the need for businesses to adopt greener manufacturing processes to meet both environmental standards and consumer expectations.
A great example of this balance is Miro Printing & Graphics Inc., which successfully integrates both laser and die cutting technologies while maintaining a strong focus on sustainability. Their operations emphasize energy efficiency and sustainable material sourcing, proving that environmental responsibility can coexist with quality and performance.
Ultimately, the choice between die cutting and laser cutting should depend on the specific needs of your project, with careful consideration of energy use, waste reduction, and material efficiency. Opting for an eco-conscious provider ensures your manufacturing aligns with sustainable practices and resonates with consumer values.
FAQs
What is the environmental impact of laser cutting compared to die cutting?
Laser cutting tends to use less energy per unit and works more efficiently compared to die cutting, which can help reduce its overall impact on the environment. Plus, it produces less material waste since it doesn’t rely on physical cutting tools, making it a more eco-friendly choice for many applications.
In contrast, die cutting can lead to more waste due to the need for custom dies and leftover materials. Even so, it remains a practical option depending on the project’s specific needs and the materials involved. Both methods have their strengths, but laser cutting often shines for its precision and smaller environmental footprint.
How do die cutting and laser cutting differ in terms of waste production?
When it comes to waste production, die cutting and laser cutting take very different approaches due to how they work. Laser cutting stands out for its precision, allowing for detailed designs with minimal material removal. This precision helps keep waste to a minimum. In contrast, die cutting often generates more waste because it relies on physical tools and larger, less optimized die shapes. This can lead to more material being discarded, especially during smaller production runs.
Another key difference lies in tooling. Laser cutting operates digitally, so there’s no need for physical tools, making it a more efficient choice for small-to-medium volume projects. However, it’s worth noting that the heat generated during laser cutting can create heat-affected zones, which might limit the reusability of leftover materials. On the other hand, die cutting requires specific tools and setup, which can introduce inefficiencies, particularly for low-volume jobs.
In short, laser cutting tends to be more efficient with materials, while die cutting often results in more waste, depending on the scale and complexity of the project.
When is die cutting a better choice than laser cutting, even though it has a higher environmental impact?
Die cutting is often the go-to method for producing simple shapes in high volumes. Known for its precision and efficiency, it’s a solid choice for large-scale projects where consistency is key. While it might produce more waste and consume more energy compared to laser cutting, its ability to perform repetitive tasks quickly and accurately can make it a more practical option in many cases.
This method also shines when creating shapes with tight tolerances, especially in projects where speed and uniformity are non-negotiable. For smaller quantities or designs that require intricate details, laser cutting might be a better fit. But for straightforward, large-scale production, die cutting remains a dependable and effective solution.
Related posts
- How Die-Cutting Impacts Waste Reduction
- How Digital Die-Cutting Works for Packaging
- Latest Trends in Automated Die-Cut Packaging Production
- Die-Cutting vs Laser Cutting: Material Differences
https://app.seobotai.com/banner/banner.js?id=6855f98d5559d477e76135b5
