Legal printing compliance is about more than just printing documents – it’s about following strict laws, regulations, and standards to avoid penalties, protect sensitive information, and maintain credibility. Here’s what you need to know:
- Understand the Laws: Identify applicable regulations like HIPAA, Privacy Act, or court-specific mandates. For example, HIPAA violations can cost $100–$50,000 per incident.
- Classify Documents: Sort data into categories like PII, sensitive PII, or PHI to apply the correct security measures (e.g., encryption, access control).
- Secure Printing Workflow: Use encryption, secure print release, and physical safeguards to protect data during printing and handling.
- Ensure Quality: Follow formatting standards (e.g., 12-point font, 1-inch margins) and use court-approved templates to produce clear, accurate documents.
- Work With Trusted Providers: Choose SOC 2 or HIPAA-certified printing partners who use advanced security protocols like AES-256 encryption.
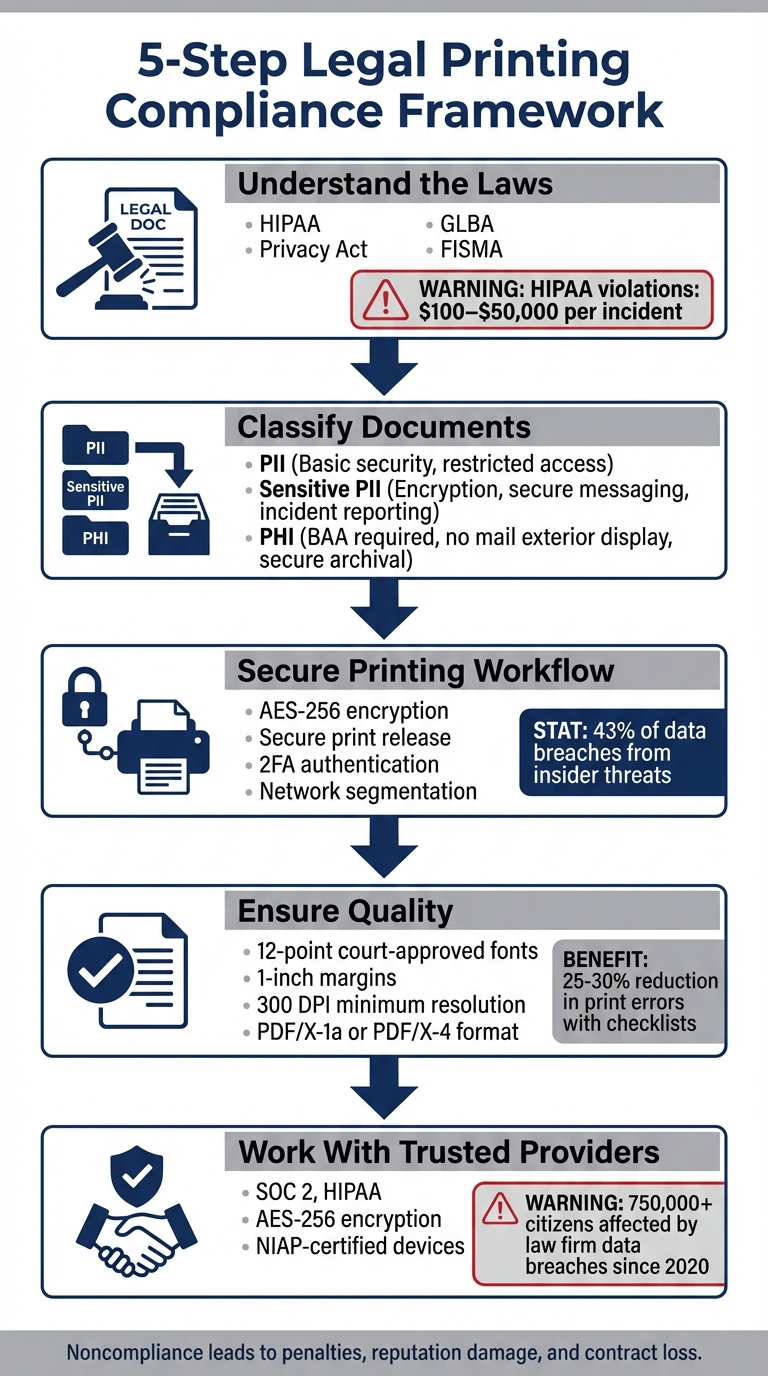
5-Step Legal Printing Compliance Framework
What Compliance Documentation Is Required To Be Maintained? – CountyOffice.org
Understanding Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Before diving into printing, it’s crucial to identify the laws that apply to your specific situation. The legal framework for printing can be intricate, involving federal statutes and privacy laws that vary depending on what you’re printing and who the intended audience is.
Federal laws lay the groundwork for compliance. For instance, the Privacy Act of 1974 regulates how federal agencies handle personal information, while HIPAA’s Privacy and Security Rules govern the management of Protected Health Information (PHI). The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) focuses on financial records, FISMA applies to federal information systems, and Title 44 U.S.C. oversees the Government Publishing Office and the distribution of public documents.
Noncompliance can lead to severe civil and criminal penalties, tarnish reputations, and even jeopardize government contracts.
Identifying Applicable Laws and Standards
Understanding your organization’s position under relevant regulations is the first step. For example, healthcare providers, health plans, or healthcare clearinghouses are classified as "Covered Entities" under HIPAA. If you’re a printing vendor handling PHI for these entities, you’re considered a "Business Associate" and are required to sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
Next, identify the types of data involved. This could include:
- PHI: Names, Social Security numbers, medical records.
- PII: Names, email addresses.
- Sensitive PII: Full Social Security numbers, biometric data, financial details.
Creating a requirements matrix can simplify compliance. For example, healthcare billing documents must adhere to HIPAA rules, court filings need to follow specific jurisdictional formatting, and federal records often require compliance with NARA digitization standards under 36 CFR Part 1236. The matrix should also assess the "Confidentiality Impact Level" of each data type – Low, Moderate, or High – to determine the necessary security measures.
Conducting a Privacy Threshold Analysis can help identify PII, and if needed, a full Privacy and Civil Liberties Impact Assessment can evaluate risks and establish safeguards. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of costly compliance errors.
Once the legal framework is clear, classify your documents based on sensitivity to define the precise security protocols.
Classifying Documents by Sensitivity
Using the legal requirements as a foundation, classifying data ensures you apply the right level of security. This prevents over-securing low-risk documents and under-securing sensitive ones.
Start by understanding data categories. For instance:
- Standard PII requires basic security measures and restricted access to authorized personnel.
- Sensitive PII demands encryption during transmission, secure communication methods, and incident reporting.
- PHI requires additional safeguards, such as Business Associate Agreements, restrictions on displaying information on mail exteriors, and secure archival systems.
Document type also affects handling requirements. For example, wills and power of attorney documents often require single-sided printing to ensure clarity and avoid disputes over missing or altered pages. Court submissions typically need to be single-sided to avoid scanning issues during digital processing. While private contracts may allow double-sided printing, sensitive financial agreements often follow single-sided formats for similar reasons.
| Classification Level | Handling Rule Examples |
|---|---|
| Personally Identifiable Information (PII) | Basic security measures; limited access to authorized users |
| Sensitive PII | Encryption during transmission; secure messaging; incident reporting |
| Protected Health Information (PHI) | Requires BAA; no display on mail exteriors; secure archival |
Inventorying your documents is key to understanding their content, context, and restrictions. This "intellectual control" ensures you apply the right security measures from the start. For instance, digitizing permanent federal records requires meeting NARA’s FADGI three-star standards, with minimum resolutions of 300 ppi for textual records and 400 ppi for photographic prints.
"Insecure data handling infrastructure can lead to a number of mishaps – making it mandatory to get yourself a HIPAA-compliant services provider." – PostGrid
Proper classification isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about protecting your clients, upholding professional standards, and keeping sensitive information secure throughout the printing process. When done right, classification ensures you activate the appropriate security measures, whether that’s secure print release, restricted physical access, or encrypted data transmission.
Building a Secure Printing Workflow
Once documents are classified, the next step is creating a secure workflow that ensures compliance throughout the printing process. This workflow addresses three key vulnerabilities: data in transit, unattended documents, and physical access to sensitive materials. It transforms legal document classification into practical security measures.
Securing Data During Printing
Encryption is your strongest safeguard. Protect data in transit using SSL/TLS protocols, and encrypt spool files at rest with AES-256-GCM, assigning unique job-specific keys for added protection.
For authentication, start with PINs for a basic layer of security. For more sensitive documents, consider ID cards or biometric scans. To ensure maximum security, implement two-factor authentication (2FA), combining methods like an ID card with a PIN or incorporating biometric verification.
Network segmentation is another critical step. Isolating mobile printing traffic from other network activities helps safeguard confidential case files and client communications.
"The moment you press print, your print job goes from a digital idea to a steal-able, forgettable, lose-able, possibly irreplaceable physical document." – Kieron Byatt, Tech journalist, PaperCut
Don’t forget about hardware disposal. Before decommissioning printers, securely wipe their hard drives to eliminate any chance of data recovery. This ensures that sensitive information can’t be reconstructed after the equipment is sold or discarded.
Implementing Secure Print Release
While encryption and authentication protect digital data, secure print release ensures that only authorized individuals retrieve physical documents.
Secure print release, also known as "pull printing", solves a common issue in legal offices: abandoned print jobs. Documents remain in a hold-and-release queue until the authorized user is physically present to retrieve them. This prevents sensitive files from being left unattended.
Authentication at the printer – whether via PINs, badges, mobile verification, or biometric scans – ensures only the intended recipient can access the document. Features like find-me printing add flexibility by allowing users to release their jobs from any authorized printer on the network, reducing the risk of sensitive documents being printed in unintended locations.
Audit trails are another essential component. Detailed logs tracking the origin, time, user, and document details for each print job not only support regulatory audits but also help identify potential security breaches. Adding digital signatures or watermarks to printed documents can enhance traceability, linking them directly to their source.
Beyond security, organizations using secure print release often see additional benefits, including up to 15% savings by reducing uncollected or duplicate print jobs. To further enhance security, configure systems to delete print jobs and sensitive metadata immediately after release.
Managing Physical Access and Chain of Custody
Even the best digital safeguards fall short if physical document security is neglected. Protecting physical files is just as important as securing digital data to ensure compliance with legal printing standards.
Store sensitive documents in locked cabinets within restricted areas, and keep office doors secured at all times. Conduct regular audits of printing facilities to verify that measures against unauthorized access, tampering, and theft are in place.
For transporting documents, follow strict protocols. Avoid leaving sensitive paperwork in vehicles or unattended during transit. When shipping document batches or hard drives, use encrypted media and trusted delivery services offering real-time tracking. For legal mail requiring a verifiable chain of custody, services like USPS Certified or Registered Mail provide mailing proofs and delivery confirmations.
Proper disposal is the final step in maintaining security. Misprints or extra copies should be destroyed immediately through shredding or controlled burning, following PCI-compliant methods to ensure discarded files cannot be reconstructed. Insider threats account for 43% of all data breaches, making strict, documented procedures for handling and disposing of sensitive materials a necessity.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) adds another layer of security by ensuring that access to both physical and digital document systems is limited to individuals based on their specific roles within the organization.
sbb-itb-ce53437
Ensuring Quality and Accuracy in Legal Printing
Security measures in your printing workflow are essential, but they lose their value if the printed documents fail to meet basic quality standards. Legal documents demand clarity and precision – every detail must be easy to read and verify, whether it’s for court proceedings or opposing counsel. Building on secure workflows, achieving high-quality printing is a key requirement for legal compliance.
Defining Quality Standards for Legal Documents
As Adobe emphasizes, "Legal documents need to be clear and legible. That’s why it’s important to use type styles that look clean and professional". Fonts like Arial, Century, Verdana, Adobe Caslon Pro, and Adobe Sabon are court-approved and project professionalism. While Times New Roman and Calibri are acceptable, they are not the preferred choices. Steer clear of novelty fonts like Comic Sans, as they can harm the credibility of your document.
Stick to a 12-point font size, which strikes a balance between readability and efficient use of space, ensuring filings aren’t unnecessarily lengthy. Margins should typically be 1 inch on all sides unless specific court rules state otherwise.
Paper size matters, too. Most legal documents use 8.5" x 14" paper (legal size) to accommodate elements like signature blocks, while 8.5" x 11" paper is suitable for correspondence or reference materials. Pre-approved templates are invaluable for maintaining consistent fonts, sizes, and margins across all documents.
Setting Up Review and Approval Processes
Once your document design aligns with legal standards, a thorough review process is critical to ensure accuracy. Implementing a standardized checklist can reduce print errors by 25–30%. Proofs should meet a minimum resolution of 300 DPI and use CMYK color mode to prevent color inconsistencies. Save files in standardized formats like PDF/X-1a or PDF/X-4 to maintain compatibility and quality.
Contract proofs are essential for confirming quality. Whether digital, physical, or video-based, these proofs must accurately reflect the final product. Always secure written client approval before moving forward with production. As Emma Davis from 4over4 explains, "A clear proof approval process protects both you and your clients. Thorough documentation helps prevent scope creep and ensures everyone is on the same page". For more intricate projects, such as bound documents, requesting video samples can help verify the layout and binding before final production.
Monitoring production adds an extra layer of assurance. Regular visual inspections, along with densitometry measurements, ensure consistent ink density and legibility throughout the print run. Registration marks are crucial for confirming that multi-color elements are perfectly aligned. Finally, perform standardized tests to check dimensions and binding integrity before approving the final output.
Working with a Compliant Printing Provider
When it comes to compliance, partnering with a secure and certified printing provider is non-negotiable. Since 2020, over 750,000 U.S. citizens have had their personal data exposed due to hacks targeting law firms. This makes it critical for your printing provider to bolster your compliance protocols.
Evaluating Provider Capabilities
The first step is to confirm that your provider holds the necessary industry certifications. SOC 2 compliance is a must – this certification ensures providers undergo regular audits by licensed CPA firms to assess security, availability, and processing integrity. These reports need to be updated annually. If your firm deals with protected health information, HIPAA certification is equally important. Be sure to request the latest audit documents to verify their data protection measures.
Additionally, confirm that the provider employs AES-256 encryption to secure data both in transit and at rest. They should also use NIAP-certified devices with automated firmware updates to guard against vulnerabilities.
"SOC 2 certification requires a printer service provider (PSP) to undergo regular audits… Printers who work with patient data or records are subject to the same HIPAA standards as healthcare and insurance providers."
– Michelle Weir, Quantum Group
Another factor to consider is in-house capabilities, which minimize risks by keeping all processes within a single secure facility. For example, Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. ensures compliance by handling bindery, mailing, digital, and offset printing services on-site. If your work includes appellate documents, make sure the provider is familiar with technical requirements such as the Federal Rules of Appellate Procedure (FRAP), which dictate specifications for paper quality, binding methods, and cover colors.
Once you’ve verified these capabilities, the next step is to align their strengths with your internal compliance processes.
Coordinating for Compliance
After confirming a provider’s certifications and security measures, it’s essential to integrate their systems with your compliance strategy. A compliant printing provider extends your secure workflow beyond your office, ensuring stringent controls are maintained throughout the process.
Work together to align their automated purge settings and data retention policies with your firm’s requirements. When managing sensitive client data, secure printing isn’t just a convenience – it’s a critical component of your compliance framework.
Consider using managed print services to centralize operations and enable real-time monitoring. This approach strengthens the chain of custody and provides documentation that can be invaluable during regulatory investigations. Regular audits of your provider’s facilities are also important to ensure ongoing compliance. Collaborate on shared Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that cover every aspect of the process, from initial design to final inspection, and update them as regulations evolve.
Conclusion
Staying compliant with legal printing requirements is an ongoing responsibility that safeguards your firm against fines, reputational damage, and security breaches. It all begins with identifying the specific laws and standards that apply to your documents – whether it’s ISO 12647 for process control or HIPAA for healthcare-related materials.
From there, securing your workflow is key. Tools like AES-256 encryption, secure print release mechanisms, and physical access controls help ensure an unbroken chain of custody from document creation to delivery. Adding quality control measures – such as defined tolerances, routine review cycles, and adherence to ISO standards – ensures every page aligns with legal requirements.
"Process control brings print processes into compliance with industry standards and guidelines and helps companies maintain consistency throughout a print run and from job to job."
– X-Rite
Working with a dependable printing partner is another essential piece of the puzzle. A trusted provider, such as Miro Printing & Graphics Inc., can seamlessly integrate your processes and strengthen your compliance efforts.
FAQs
What happens if legal printing doesn’t meet compliance requirements?
Failing to meet legal printing requirements can lead to serious consequences – think hefty fines, potential lawsuits, and other legal challenges. But it doesn’t stop there. Ignoring these requirements can tarnish your business’s reputation and erode trust with clients and partners.
By staying compliant, you’re not just avoiding trouble – you’re showing that your organization values professionalism and takes the responsibility of managing sensitive legal documents seriously.
How can I ensure my printing provider meets all legal and compliance requirements?
To make sure your printing provider meets legal and industry standards, here’s what you should do:
- Check compliance with federal regulations: Ensure the provider follows federal printing laws, which may include rules about handling sensitive documents or limits on duplication.
- Look for ISO certification: Confirm the provider adheres to relevant ISO standards, such as those for process control or ink color accuracy, to guarantee quality and compliance.
- Verify privacy and security measures: If your documents contain sensitive or confidential information, make sure the provider has safeguards like secure handling, encryption, and privacy protocols.
- Request proof of compliance: Ask for documentation, such as a compliance statement or a recent audit report, to confirm they meet legal and industry requirements.
- Inspect their operations: If possible, visit their facility or arrange a virtual tour to check for secure environments, properly calibrated equipment, and appropriate handling of restricted materials.
For a dependable option, Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. offers complete printing services while maintaining strict adherence to all legal and industry standards, ensuring your printing needs are met with care and professionalism.
How can I classify legal documents based on their sensitivity?
Classifying legal documents based on sensitivity is all about analyzing their content and assigning labels that safeguard both compliance and security. Start by examining what type of information each document holds – this could range from personal data and financial records to confidential legal details. Once you’ve identified the content, sort the documents into categories like public, internal use only, confidential, or highly confidential.
To stay aligned with regulations such as HIPAA or GDPR, it’s essential to create clear internal guidelines for how documents are classified and handled. This includes measures like secure storage, limiting access to authorized personnel, and ensuring proper labeling practices are in place. For a more customized approach, consider consulting industry-specific compliance resources or seeking advice from legal professionals to ensure your process fits your organization’s unique requirements.
Related Blog Posts
- Post-Press Quality Control Checklist
- Common Post-Press Quality Issues and Fixes
- ISO 2846: Ink Color Standards Explained
- Proofing Standards in Printing: Key ISO Guidelines
https://app.seobotai.com/banner/banner.js?id=694dd55012e0ddc125009be9
