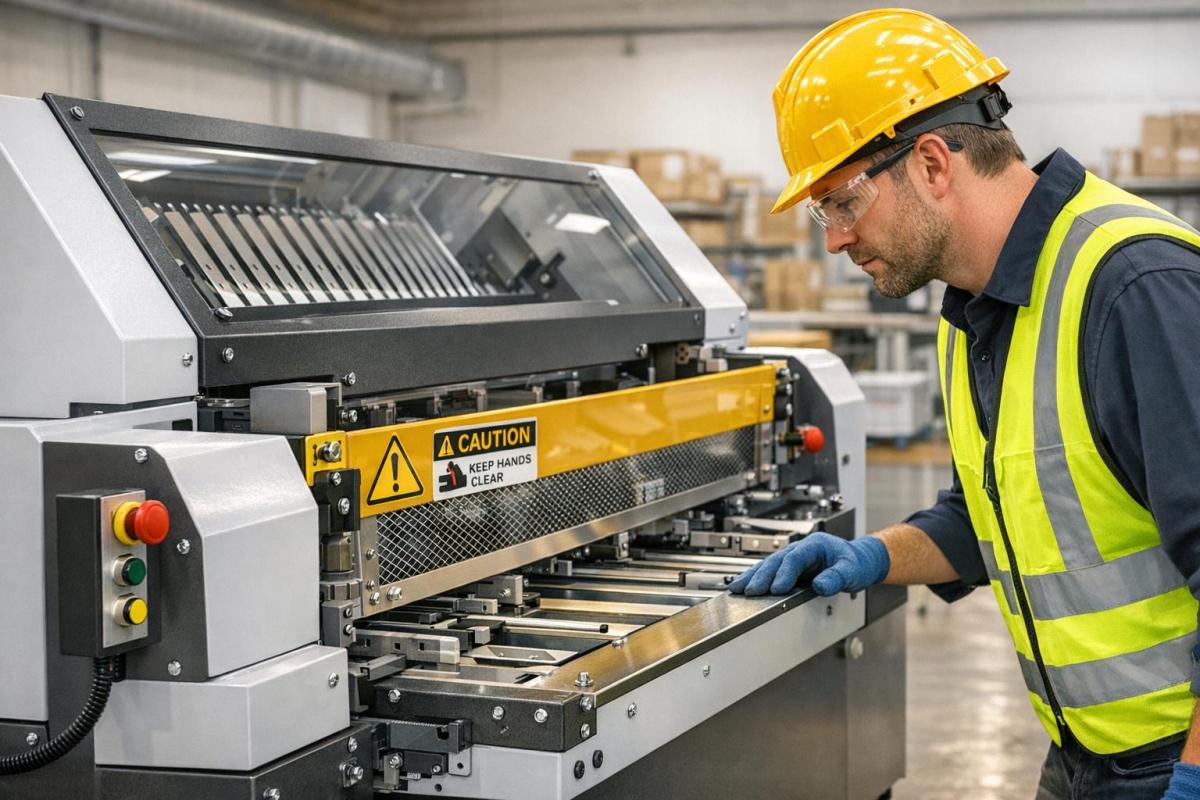
Folding machines are essential in print shops but pose serious safety risks like crushed fingers, amputations, and blindness if not properly managed. OSHA‘s updated safety standards, including 29 CFR 1910.212 and the National Emphasis Program (NEP) on amputation hazards, emphasize the need for safeguards to protect workers. Here’s what you need to know:
- Key Hazards: Ingoing nip points, rotating parts, flying debris, and maintenance-related risks.
- Safety Measures: Barrier guards, two-hand tripping devices, and Lockout/Tagout procedures are required to reduce risks.
- Regulations: OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.212 and ANSI B11 standards outline essential safety practices.
- Employee Training: Workers must be trained on machine-specific risks and safety protocols.
- Inspection & Maintenance: Regular checks and maintenance ensure machines remain safe and functional.
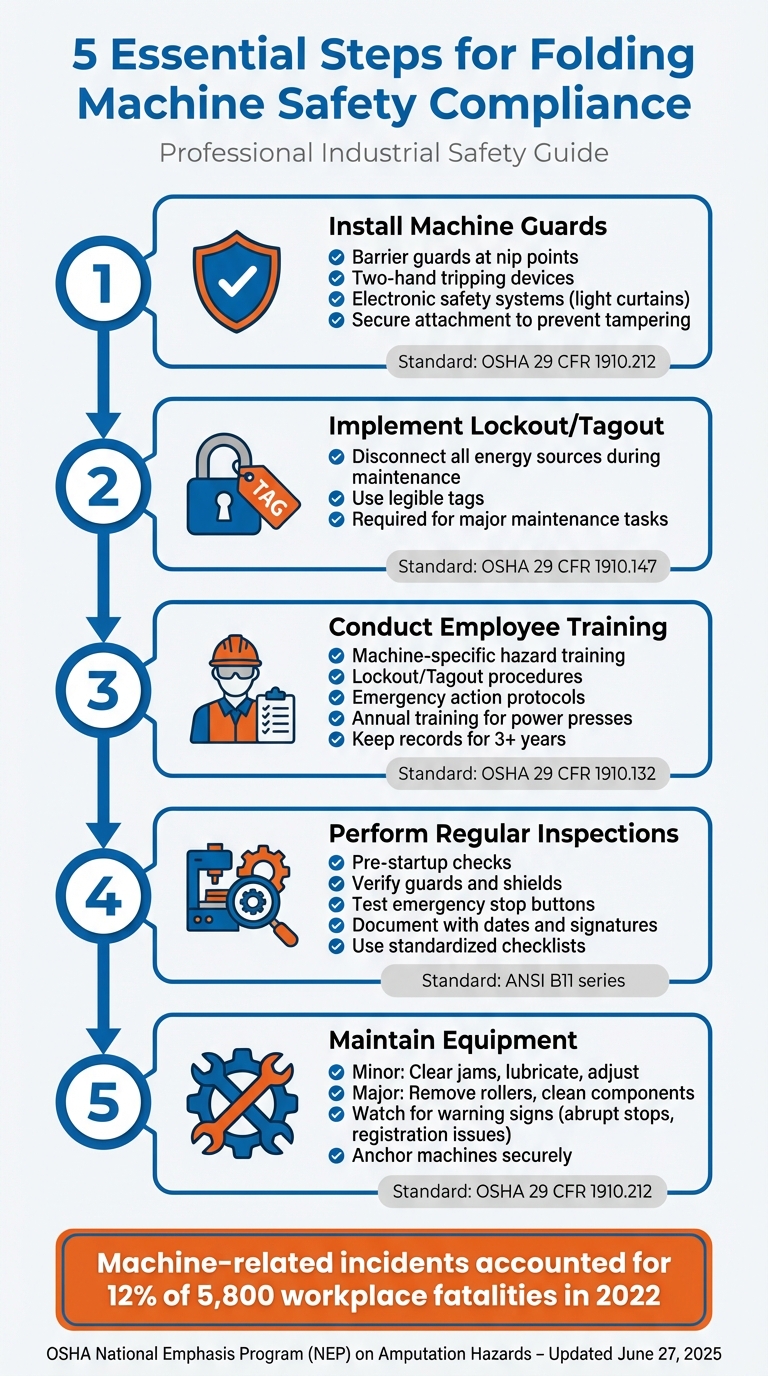
5 Essential Steps for Folding Machine Safety Compliance
OSHA Guidelines for Folding Machine Safety
OSHA Machine Guarding Requirements
OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.212 outlines essential guidelines for machine guarding, which extend to folding machines even though no specific regulation exists for them. According to OSHA’s standard:
"One or more methods of machine guarding shall be provided to protect the operator and other employees in the machine area from hazards such as those created by point of operation, ingoing nip points, rotating parts, flying chips and sparks." – OSHA 29 CFR 1910.212(a)
Guards should be securely attached to the machine or a stable structure to ensure safety and must not introduce new hazards. For stationary equipment, proper anchoring is critical to prevent movement during operation.
The regulation emphasizes guarding the point of operation – the area where material is processed – to keep operators from accidentally placing body parts in dangerous zones during machine use. While supplementary tools can assist with feeding or removing materials, they are not substitutes for required guarding measures.
These general safety requirements form the basis for more specific protections tailored to folding machines.
Folding Machine-Specific Safety Rules
Folding machines come with their own risks, particularly at ingoing nip points and where folding blades meet the machine bed. To address these hazards, consider using barrier guards, two-hand tripping devices, or electronic safety systems like light curtains.
Beyond physical safeguards, OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.147 enforces Lockout/Tagout procedures to ensure folding machines are entirely disconnected from energy sources during servicing or maintenance. Additionally, operators must wear appropriate eye and face protection, as required by OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.133, when exposed to flying particles or sparks.
Although ANSI B11 series standards are not legally enforceable, OSHA frequently references them as valuable resources for improving machine safety practices.
Companies in industries like printing, such as Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. (https://bergencountyprinters.com), can apply these OSHA guidelines to maintain safe and compliant folding machine operations while aligning with industry standards.
Common Hazards and Prevention Methods
Typical Hazards in Folding Machine Operations
Operating folding machines comes with several risks, particularly at the point of operation, where tasks like bending or folding materials happen. If an operator’s body part accidentally enters this area during a machine cycle, serious injuries can occur. Another danger arises from ingoing nip points, which form where rotating parts – like feed rollers or folding cylinders – meet or align near fixed objects. These points can snag clothing, hair, or even limbs, pulling them into the machinery.
Other threats include moving parts, reciprocating motions, and flying debris. Maintenance work adds its own risks, such as unexpected energy releases or exposure to ungrounded electrical components. Additionally, secondary hazards like slips, trips, and prolonged exposure to loud noise can lead to workplace injuries. In fact, machine-related incidents made up more than 12% of the 5,800 workplace fatalities reported in 2022.
Prevention Methods and Safety Practices
To mitigate these risks, proper machine guarding is essential. Barrier guards, two-hand tripping devices, and electronic systems like light curtains are effective at keeping workers safe. Sam Poon, an Industrial Automation Expert at Pacific Blue Engineering, emphasizes the importance of robust guarding:
"Guards should prevent workers’ hands, arms, or other body parts from making contact with dangerous moving parts. They must be durable, secure, and difficult to remove or tamper with."
Additional safeguards include placing emergency stop buttons within easy reach, securing machines to the floor to prevent unexpected movement, and ensuring fan blades located less than seven feet above the floor are guarded with openings no larger than half an inch. Regular inspections ensure guards remain in place and functional, while specialized hand tools can help operators handle materials without putting themselves at risk. However, these tools should only complement primary safety measures.
Companies like Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. (https://bergencountyprinters.com) demonstrate how adopting comprehensive safety practices can protect workers while maintaining productivity. Beyond physical safeguards, thorough employee training is critical for fostering a safe and efficient workplace environment.
Employee Training and Safety Practices
Why Employee Training Is Required
While precise machine safeguards are essential, effective employee training plays a critical role in reducing the risks associated with folding machines. OSHA requires that workers be trained on each specific piece of equipment before they operate it, as machine guarding can vary significantly between models.
A solid training program should cover key areas such as mechanical motions, the correct use of barrier guards, and two-hand tripping devices. Additionally, Lockout/Tagout procedures are crucial to ensure machinery is completely de-energized during maintenance. For printing and folding operations, the "inch-safe-service" technique provides a safer way to make machine adjustments. OSHA also specifies that training for mechanical power presses must be conducted annually, with records of this training kept for at least three years.
| Training Topic | Key Components | OSHA Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Guarding | Point of operation, nip points, rotating parts | 29 CFR 1910.212 |
| Lockout/Tagout | Energy control, legible tags | 29 CFR 1910.147 |
| PPE | Proper use, limitations, maintenance | 29 CFR 1910.132 |
| Emergency Action | Evacuation plans, reporting, contact protocols | 29 CFR 1910.38 |
Comprehensive training programs are the foundation of a workplace that prioritizes safety and prevention.
Building a Safety-Focused Workplace
Once training is in place, fostering a proactive safety culture becomes the next step in preventing workplace injuries. Adhering to OSHA’s standards, this approach encourages employees to actively participate in safety efforts. When workers feel empowered to report hazards and suggest improvements, the entire operation becomes safer and more efficient.
Regular safety drills are an effective way to ensure operators are prepared for emergencies. These drills should focus on critical tasks like quickly locating and using emergency stop controls, identifying danger zones, and following proper procedures when safety features are damaged or malfunctioning. Routine inspections of machine guards are equally important to confirm that all safety mechanisms are securely attached and functioning as intended. For facilities involved in folding operations, using standardized checklists based on ANSI/ASSP Z490.1 criteria ensures that training programs meet established industry standards. By integrating safety into daily routines, businesses can reduce injuries while boosting overall productivity.
At Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. (https://bergencountyprinters.com), thorough employee training and rigorous safety inspections are key to maintaining both a secure and efficient workplace.
sbb-itb-ce53437
Inspection and Maintenance Procedures
Regular Inspection Procedures
Before starting up a folding machine, it’s crucial to perform a thorough inspection and document any issues that arise.
An effective inspection should focus on several key areas. First, ensure all safety guards and shields are properly installed and functioning. Test foot pedals, controls, and emergency stop buttons to confirm they can halt the machine immediately if needed. Additionally, check the back gauge, die alignment, and any potential pinch points to prevent accidents. As Oxmaint emphasizes:
"A comprehensive inspection and maintenance of bending machines is essential to reduce workplace hazards, ensure operator safety and maintain optimal machine performance".
To maintain consistency, use a detailed checklist that includes equipment identification, operating hours, and operator acknowledgment. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) – such as safety gloves, glasses, and shoes – is mandatory for both inspectors and operators to minimize risks. These inspections should comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.212 and the ANSI B11 series standards.
Once inspections are complete, regular maintenance is the next step to ensure machines remain safe and efficient.
Maintenance Procedures and Schedules
Maintenance tasks can be divided into two categories: minor and major. Minor tasks include clearing jams, applying light lubrication, and making small adjustments using the inch-safe-service technique during production. Major tasks, such as removing rollers and cleaning internal components like frames and braces, require a full lockout/tagout procedure to prevent accidental activation.
Watch for warning signs like abrupt stops at the fold plate, registration issues, or excessive static buildup, as these often indicate wear. Andre Palko, Founder of Technifold USA, points out:
"80% of most problems can be traced to only 20% of the possible causes, most of which are simple. In many of the calls I receive, the fix is obvious… or a call to the mechanic for a tune-up or quick repair is all that’s needed".
Regular cleaning is particularly vital in dusty environments, where debris on rollers can lead to malfunctions. Machines that are permanently installed should also be securely anchored to prevent movement during operation, which could cause misalignment and pose safety risks.
Both inspection and maintenance procedures must align with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.212 and the ANSI B11 standards, ensuring compliance with established safety regulations.
Machine Guarding Safety Training | Stay Protected | Workplace Safety Certification
Conclusion
Ensuring safety around folding machines isn’t just a legal obligation – it’s a critical step in protecting workers from potentially life-altering injuries. Employers are required to comply with OSHA standards, specifically 29 CFR 1910 Subpart O and 29 CFR 1910.147, to safeguard employees from hazards posed by moving machine parts.
As OSHA highlights:
"Safeguards are essential for protecting workers from these preventable injuries. Any machine part, function, or process that may cause injury must be safeguarded."
Failing to implement proper safety measures can lead to devastating injuries, such as crushed fingers, amputations, burns, or even blindness – many of which are entirely avoidable with adequate precautions and training. OSHA has taken this issue seriously, establishing a National Emphasis Program (NEP) to address amputation risks in manufacturing. The program’s most recent updates were issued on June 27, 2025.
Aside from meeting legal requirements, strong safety protocols offer practical benefits for businesses. They can reduce lost workdays, lower insurance costs, and minimize the expenses tied to hiring and training replacement workers. As OSHA’s Printing Industry eTool puts it, “Good ergonomics is good business”.
Effective safety practices hinge on three key elements: proper machine guarding, thorough training, and regular inspections. Safeguards must prevent operators from accessing hazardous areas during machine use. Comprehensive training equips employees to operate machinery safely and recognize workplace-specific risks. Meanwhile, documented inspections, complete with dates, signatures, and machine serial numbers, ensure that equipment remains in safe working condition.
While OSHA provides the federal baseline for safety, some states enforce stricter regulations. Employers should review local requirements to ensure full compliance. For additional support, OSHA offers free safety consultations to help employers identify risks and strengthen their safety programs.
At Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. (https://bergencountyprinters.com), we place safety at the forefront of our operations. By adhering to – and often exceeding – industry standards, we not only protect our team but also ensure that our printing and post-press services remain reliable and efficient. This unwavering commitment to safety is a cornerstone of our operational culture.
FAQs
What are the key safety risks when using folding machines?
Folding machines play a crucial role in printing and finishing operations, but they can present safety risks if not handled correctly. Some common dangers include injuries to hands or fingers from moving parts, getting caught in the machine due to loose clothing or jewelry, and accidents stemming from poor maintenance or faulty safety mechanisms.
To reduce these risks, operators should strictly adhere to OSHA guidelines, regularly inspect the equipment, and ensure safety guards and emergency stop features are in place and functional. Providing thorough training for all operators is equally important to create and maintain a safe working environment.
What is OSHA’s Lockout/Tagout procedure, and how does it improve folding machine safety?
OSHA’s Lockout/Tagout procedure is a critical safety measure designed to protect workers during maintenance or servicing of equipment like folding machines. It ensures that all energy sources – whether electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic – are completely isolated and locked out, preventing unexpected start-ups or energy releases.
By implementing this procedure, businesses can greatly reduce the risk of workplace injuries, creating a safer environment for both operators and maintenance teams. Beyond safeguarding employees, adhering to these safety protocols also keeps companies in line with regulatory requirements, reinforcing their commitment to workplace safety.
Why is proper training essential for safely operating folding machines?
Proper training is essential for safely operating folding machines because it equips employees with the skills to recognize and handle potential risks. Workers gain an understanding of how to properly use safety features like guards, interlocks, and lockout/tagout procedures, all of which are mandated by OSHA regulations. This not only helps reduce the likelihood of accidents but also ensures the workplace meets required safety standards.
Beyond safety, training has a direct impact on productivity. Skilled operators can avoid equipment misuse, reduce downtime, and handle routine maintenance more effectively. A well-trained team creates a workplace culture that prioritizes safety, safeguarding both employees and machinery while keeping operations running smoothly.
Related Blog Posts
- 5 Tips to Prevent Cracking on Folded Prints
- How Folding Machines Handle Complex Print Layouts
- Top Folding Machines for High-Volume Printing
- Designing for Safety: Die-Cut and Laser-Cut Tips
https://app.seobotai.com/banner/banner.js?id=696983f40a871bef4ad18895
