Direct mail campaigns can deliver an impressive 112% ROI, outperforming many digital methods. To achieve this, it’s vital to allocate your budget effectively and focus on key areas like postage, printing, design, and mailing lists. Here’s what you need to know:
- Postage: Often the largest expense, ranging from $0.31 to $0.58 per piece. Marketing Mail is cheaper but slower, while First-Class Mail is faster but costs more.
- Printing: Costs vary by format, from $0.05 to $1.00 per piece, depending on materials and methods (digital vs. offset printing).
- Design: Professional services cost $150 to $1,000 per project, but templates or in-house work can lower expenses.
- Mailing Lists: High-quality lists cost $0.03 to $0.30 per record and determine up to 40% of your campaign’s success.
Targeting the right audience, such as repeat customers or those undergoing life changes, boosts response rates. Personalization – like using names or tailored offers – can increase engagement by up to 500%. Testing small batches before scaling ensures better results and minimizes risks.
To measure success, track metrics like ROI, response rates, and cost per acquisition (CPA). Tools like QR codes or unique URLs help connect offline campaigns to online conversions. By carefully managing costs and analyzing performance, direct mail can become a reliable revenue driver.
Direct Mail Strategies to Boost ROI & Cut Costs
Breaking Down Direct Mail Costs
To manage your budget effectively, it’s essential to know exactly where your money is going. Postage often takes the largest chunk, sometimes surpassing what you spend on printing. Beyond that, you’ll need to factor in costs for design, production, and mailing lists. Let’s break it down.
On average, marketers spend between $0.65 and $3.00 per piece for a complete direct mail campaign.
Printing and Production Expenses
Printing costs can vary widely. For instance, postcards typically cost $0.03 to $0.08 per piece, brochures range from $0.06 to $0.18 per piece, and personalized envelope packages can climb to $0.17 to $0.50 or more. Overall, printing expenses usually fall between $0.05 and $1.00 per piece, depending on factors like paper weight, color options, finishing touches, volume, and the printing method used.
- Digital printing is ideal for smaller print runs and allows for cost-effective personalization through Variable Data Printing (VDP).
- Offset printing, on the other hand, becomes more cost-efficient for large-scale campaigns, though it requires a higher upfront investment in printing plates.
Printing larger quantities in a single run can significantly reduce your per-piece costs by spreading setup expenses across the total volume.
Postage Expenses
Postage is almost always the biggest expense in any direct mail campaign. Keith Goodman, VP of Corporate Marketing & Sales at Modern Postcard, puts it plainly:
"In almost every campaign, the cost-per-piece of the printing will be a smaller percentage of the overall cost than the postage".
For delivery, Marketing Mail rates start at around $0.31 per piece and take 10–15 business days. If you need faster delivery, First-Class Mail costs between $0.40 and $0.58 per piece, with delivery times of 3–5 business days.
If timing isn’t critical, Marketing Mail can save you a significant amount. To keep costs low, ensure your mailpieces weigh less than 3.3 oz and meet standard USPS dimensions, such as 6"x9" postcards. This helps you avoid extra per-pound surcharges or costly "flat" fees.
Design and Mailing List Expenses
Design and mailing lists are other key contributors to your budget:
- Design Costs: Professional design services range from $100 to $300 per hour or $150 to $1,000 per project, depending on the complexity. You can save by using pre-made templates or handling design in-house, but weigh these savings against the time and quality needed for your campaign.
- Mailing List Costs: Consumer mailing lists generally cost between $0.03 and $0.10 per record, while specialty lists targeting specific behaviors can cost $0.30 or more per record. Given that the quality of your list determines about 40% of your campaign’s success, investing in a high-quality list is crucial. To cut waste and take advantage of USPS automation discounts, ensure your list is CASS-certified and updated through NCOA.
Targeting the Right Audience
Once you’ve got a handle on direct mail costs, the next step is making sure your message lands in the hands of the people most likely to respond.
Focus your resources on those who are most likely to engage. For example, house lists – your current and past customers – typically achieve a 9% response rate, compared to just 5% for prospect lists. That difference can significantly impact your campaign’s overall profitability.
Finding Your Most Profitable Segments
Your existing customers are a goldmine. They’re already familiar with your brand and have made purchases, making them far more likely to buy again than someone who’s never interacted with your business. Dive into your customer data to identify key groups like repeat buyers, recent purchasers, or those with a high lifetime value (LTV). These segments often justify a larger share of your budget because they’re more likely to convert.
Life events also present prime opportunities. People going through major changes – like moving, getting married, or having a baby – are often ready to make new purchasing decisions. Campaigns that tie into these events can see a 200% boost in performance compared to standard campaigns. By combining behavioral data (like browsing history or past purchases) with demographic details like age or income, you can refine your targeting even further.
Using Personalization to Increase Returns
Personalization doesn’t have to break the bank, thanks to tools like Variable Data Printing (VDP). This technology allows you to customize images, offers, and messages for each recipient without racking up significant costs. Even small touches, like adding a recipient’s name, can increase response rates by 135%. Including additional personal details can push those rates up to 500%.
Take thredUP as an example. They saw a 25% increase in order rates by using personalized HTML retention postcards aimed at customers who were at risk of disengaging. Anthony Marino, President of thredUP, shared:
"We’ve seen a 25% increase in order rate from the customers we target with Lob campaigns."
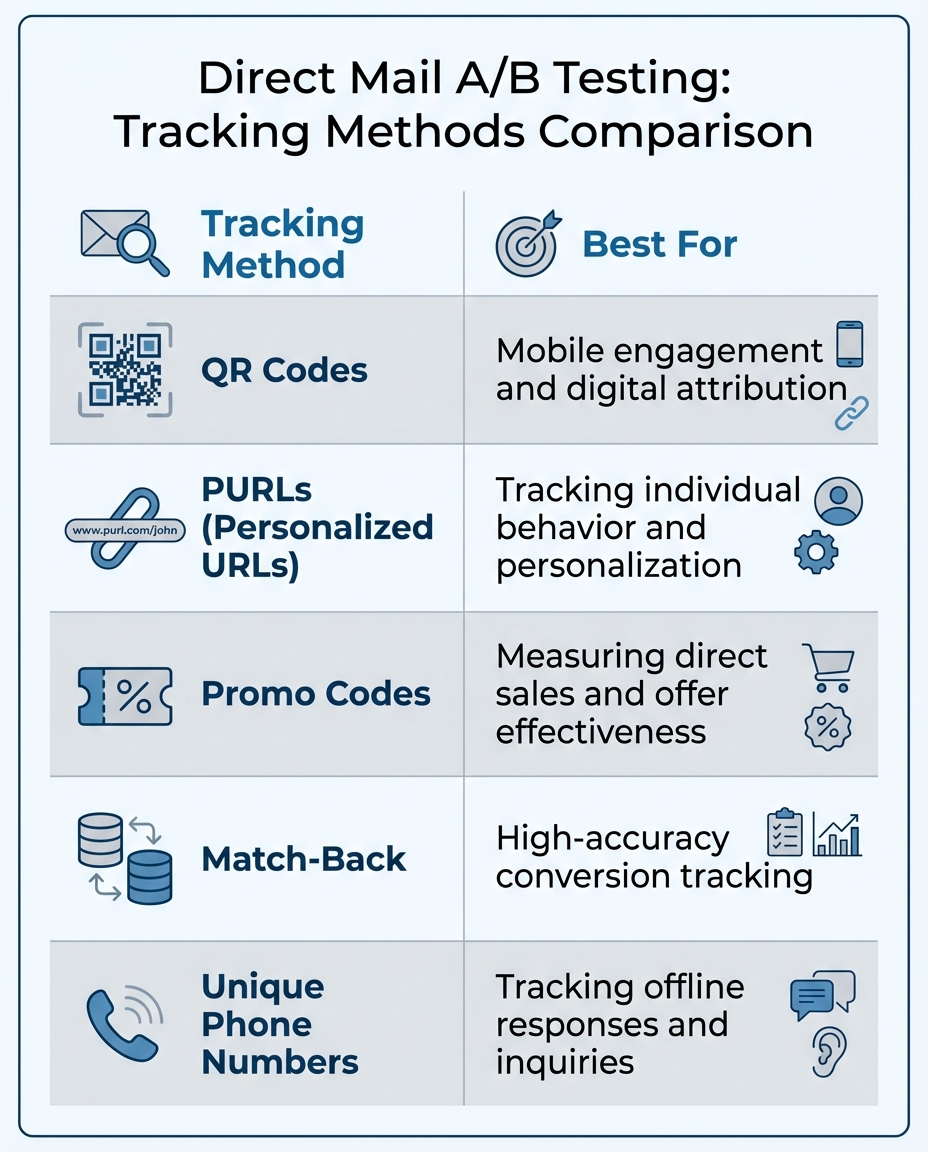
You can also integrate personalized QR codes or unique URLs (pURLs) to track individual responses. This not only connects your direct mail efforts to online activity but also gives you precise data to measure performance.
sbb-itb-ce53437
Dividing Your Budget Across Campaign Components
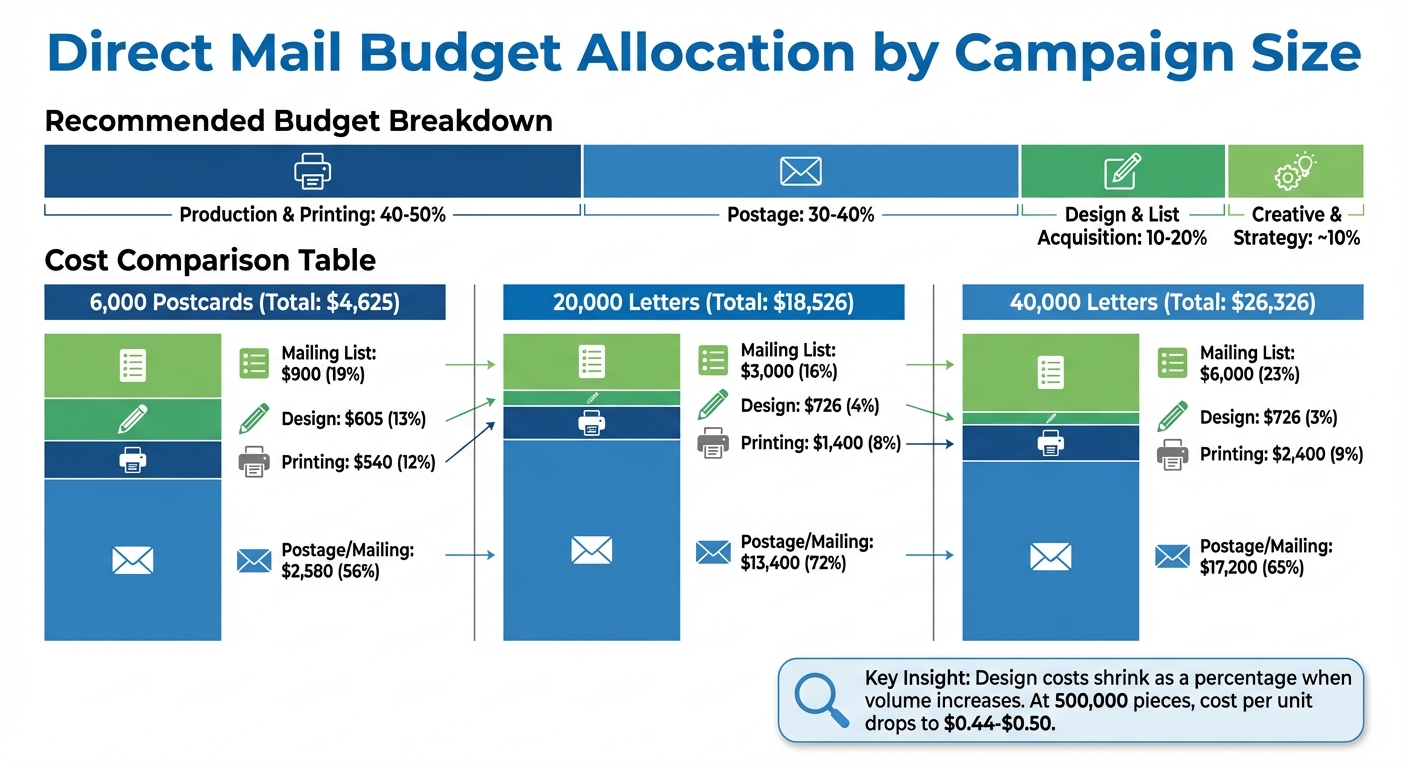
Direct Mail Budget Allocation Breakdown by Campaign Size
Once you’ve analyzed costs, the next step is dividing your budget wisely to get the best return on investment. Typically, you’ll need to allocate funds across production, postage, design, and data services.
Recommended Budget Breakdown
Direct mail campaigns generally involve four main expense categories: creative design, production and printing, mailing and postage, and list and data services. Here’s a typical budget allocation:
- 40-50% for production and printing
- 30-40% for postage
- 10-20% for design and list acquisition
Creative and strategy services usually account for about 10% of the overall budget.
Budget allocation can shift depending on campaign volume. Let’s look at an example:
| Campaign Component | 6,000 Postcards | 20,000 Letters | 40,000 Letters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mailing List | $900 (19%) | $3,000 (16%) | $6,000 (23%) |
| Design | $605 (13%) | $726 (4%) | $726 (3%) |
| Printing | $540 (12%) | $1,400 (8%) | $2,400 (9%) |
| Postage/Mailing | $2,580 (56%) | $13,400 (72%) | $17,200 (65%) |
| Total Cost | $4,625 | $18,526 | $26,326 |
Notice how design costs shrink as a percentage of the total budget when volume increases. For instance, in a 500,000-piece letter campaign, the cost per unit drops to between $0.44 and $0.50, thanks to bulk discounts and production efficiencies.
After dividing your budget, it’s crucial to test your approach before fully scaling the campaign.
Testing and Adjusting Your Budget
Testing is a key step before committing to a large-scale campaign. Set aside a portion of your budget to experiment with different creative elements, offers, and formats. While testing can result in higher costs per piece for smaller batches, it’s a smart investment to validate your strategy.
Alan Sherman, VP of Marketing Strategy at IWCO Direct, highlights the importance of bold testing:
"We find that ‘bolder’ testing, such as changing package format, leads to greater lifts in response vs. smaller iterative changes, such as changing a headline".
Focus your test budget on meaningful changes that can deliver measurable results. Once you’ve identified what resonates with your audience, you can scale up with confidence and refine your budget allocation based on real performance data.
Measuring Results and Improving Future Campaigns
Once your campaign is live, it’s time to monitor its impact and ensure your budget was well spent. Start by tracking key metrics like the Response Rate, which shows the percentage of recipients who engage with your campaign – whether that’s scanning a QR code, visiting a personalized URL, or calling a dedicated number. You can calculate this by dividing the number of responses by the number of delivered mail pieces. Another critical metric is the Conversion Rate, which measures how many of those responders take the final action you’re aiming for, like making a purchase or signing up for a service.
Return on Investment (ROI) is the ultimate measure of success. Calculate it using the formula: ((Total Revenue – Total Campaign Cost) / Total Campaign Cost) × 100. To assess how efficiently your campaign brings in customers, track Cost Per Acquisition (CPA), which is the total campaign cost divided by the number of new customers. Additionally, the Average Order Value (AOV) can reveal how much each customer spends per transaction, with direct mail often increasing AOV by building trust.
Metrics to Track
Beyond basic engagement, other metrics can provide deeper insights. For example, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) estimates the total revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with your business, which can help justify a higher initial CPA. Another useful measure is Revenue Per Mailpiece, calculated by dividing total revenue by the number of delivered mailers. This gives a quick snapshot of your campaign’s overall effectiveness.
To directly attribute sales to specific mailers, use trackable elements like unique coupon codes, QR codes, or dedicated phone numbers. For purchases that don’t use these tracking methods, match-back analysis can compare your mailing list with transaction records to identify sales driven by your campaign.
| Metric | Formula | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Response Rate | (Responses ÷ Delivered Pieces) × 100 | Measures initial engagement and interest |
| Conversion Rate | (Conversions ÷ Responses) × 100 | Evaluates how effectively responders complete your goal |
| CPA | Total Campaign Cost ÷ New Customers | Assesses cost efficiency of acquiring customers |
| ROI | ((Revenue – Cost) ÷ Cost) × 100 | Shows overall profitability of the campaign |
These metrics aren’t just numbers – they’re tools to refine your strategy and make smarter budget decisions for future campaigns.
Working with Professional Print Services
Your campaign’s performance data can also guide how you choose partners for future projects. For example, Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. offers mailing and fulfillment services that include automated inserting, addressing, and CASS certification. This certification ensures addresses are accurate, reduces undeliverable mail, and helps you qualify for USPS automation discounts. Their Every Door Direct Mail (EDDM) service is another powerful tool, allowing you to target specific geographic areas without needing to buy mailing lists.
Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. also provides an in-house bindery, offering services like UV coating, die cuts, folding, and assembly – all handled in one location. This streamlined approach eliminates delays and reduces the hassle of managing multiple vendors. When you consider the "soft costs" – like the time your staff spends coordinating with various providers – working with a full-service print shop that handles everything from design to mailing can save both time and money.
Conclusion
The strategies for cost management, precise targeting, and continuous testing all come together to create a powerful framework for direct mail success.
Think of every dollar spent on direct mail as an investment in growth. With careful planning, you can estimate profitability and customer acquisition costs before even sending out your first piece. This mindset transforms direct mail from being just another expense into a scalable channel for driving revenue. Studies consistently show that well-executed direct mail campaigns turn costs into measurable profits.
The secret lies in balancing thorough preparation with ongoing adjustments. Start by conducting a break-even analysis to determine the minimum response rate you need. Then, allocate part of your budget to test different creative approaches, offers, and audience segments. As Mike Gunderson, Founder and President of Gundir, wisely notes:
"We test because we can’t know for sure until we do. Calculators are no substitute for being in-market".
This philosophy is the backbone of any effective direct mail strategy. It ensures you avoid scaling campaigns that don’t perform while identifying the audience segments worth investing in more heavily.
Don’t overlook hidden costs like undeliverable mail or added administrative tasks. Keep your mailing lists accurate with tools like CASS certification and NCOA updates to ensure your materials reach the right people. Partnering with a full-service provider, such as Miro Printing & Graphics Inc., can also streamline production and reduce overhead costs. Over time, these efficiencies add up, and as your campaign scales, the cost per piece typically decreases.
Finally, track your campaign’s performance using tools like unique promo codes, QR codes, or personalized URLs. These tools bridge your offline efforts with online conversions, helping you measure both immediate returns and long-term customer value. By taking a long-term perspective, you can justify higher initial spending on prospects who are likely to become loyal, repeat customers. With detailed planning, consistent testing, and precise measurement, direct mail can evolve into a reliable and scalable engine for business growth.
FAQs
How can I allocate my direct mail budget to maximize ROI?
To get the most out of your direct mail campaign, it’s crucial to allocate your budget wisely across key areas: postage, printing, and design. A typical breakdown might look like this: 30% for postage, 45% for printing, and 25% for design and creative work. This balance ensures you’re investing in quality materials and effective messaging without overspending.
Looking to save on postage? Options like presorted mail or lighter formats, such as postcards, can help cut costs. For printing, opt for materials that are both affordable and durable. If you’re using variable data printing, focus it on elements that drive engagement, like personalized offers. When it comes to design, make sure your materials feature bold headlines, clear calls-to-action, and visuals that align with your brand identity. Companies like Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. offer professional printing and in-house design services to help you achieve both quality and cost efficiency.
To keep track of your spending, calculate the cost per piece by dividing your total budget by the number of mailers. Use this data to fine-tune your allocations. After your campaign wraps up, analyze the results to optimize your budget for future mailings.
What are the best ways to target the right audience for a successful direct mail campaign?
Targeting the right audience is the foundation of any successful direct mail campaign. Start by building a clear and detailed profile of your ideal customer. Combine demographics – like age, income, and marital status – with psychographics, which include interests, lifestyle choices, and purchasing motivations. You can also fine-tune your targeting by looking at recent behaviors, such as past purchases or activity on your website.
Once you’ve defined your audience, focus on using a high-quality mailing list that matches your customer profile. Whether you choose a professional list provider or opt for USPS Every Door Direct Mail (EDDM) to target specific geographic areas, having an accurate and up-to-date list is critical. A clean list ensures your mail reaches the right people and minimizes wasted time and resources.
Don’t forget to personalize and segment your mailings. Craft messages that resonate by tailoring them to factors like purchase history, individual preferences, or even local events. Personalization helps create a stronger connection with your audience, boosting response rates and delivering better returns on your investment.
Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. offers support at every stage of the process – from acquiring the right mailing list to designing, printing, and mailing your materials. They make it easy to ensure your campaign reaches the right people effectively and efficiently.
How do I track the success of my direct mail campaign to ensure a strong ROI?
To gauge how well your direct mail campaign is working, focus on tracking a few key metrics. Start with the response rate (responses divided by the number of mailers sent) and the conversion rate (conversions divided by responses). Then, look at cost per acquisition to see how much you’re spending to gain each customer, and measure the revenue generated per mailer to understand the financial impact of your efforts.
Once you’ve gathered these numbers, calculate your ROI with this formula: (Revenue – Cost) ÷ Cost × 100%. This will show you if your campaign is delivering a worthwhile return on your investment. By regularly reviewing these metrics, you can fine-tune your approach and improve the performance of future campaigns.
Related Blog Posts
- 8 Metrics to Track Direct Mail Success
- 10 Budget Mistakes in Direct Mail Campaigns
- 5 Ways to Cut Direct Mail Printing Costs
- Common Print Marketing Mistakes That Waste Money
https://app.seobotai.com/banner/banner.js?id=697019680a871bef4add889f