When it comes to printed materials, weak bindings can lead to cracked spines, loose pages, and damaged credibility. Binding strength testing ensures durability by simulating stresses like peeling and shearing to identify potential failures before products reach customers.
Key takeaways:
- Testing Methods: Pull tests, flex tests, and page fanning detect adhesive issues, weak coils, or poor binding tooth engagement.
- Common Failures: Adhesive breakdown, spine cracking, and page detachment.
- Adhesive Comparison: Polyurethane reactive (PUR) adhesives outperform traditional EVA adhesives, offering better durability, especially for coated papers.
- Industry Standards: Standards like ASTM D903 and D882 guide testing protocols, ensuring consistent results across production.
- Cost Implications: Binding failures can cost $0.50–$2.00 per reprinted unit and harm customer satisfaction.
Current Research and Testing Methods
Mechanical Testing Techniques
Researchers rely on tensile, peel, and shear tests to assess the durability of binding materials. Tensile tests involve applying a perpendicular force to measure the load required to separate pages or covers from the binding, providing insights into spine strength and page retention. Peel tests, conducted at 90° or 180°, determine the force needed to gradually separate a cover or page from the adhesive. These tests help identify whether failures occur within the adhesive itself (cohesive failure) or at the adhesive–paper interface. Shear tests, on the other hand, measure the force required to slide layers parallel to the bond line, offering a critical understanding of how well the binding holds up during handling or mailing. Together, these mechanical techniques provide a detailed picture of adhesive performance under various stress conditions.
When comparing adhesive systems, polyurethane reactive (PUR) bindings consistently outperform standard hot-melt EVA adhesives in peel and shear strength. For instance, a 2023 study revealed that PUR adhesives achieve peel strengths exceeding 10 N/cm, while EVA adhesives typically range between 2–5 N/cm. PUR adhesives also demonstrate superior performance under fluctuating temperature and humidity, making them particularly suitable for heavy coated stocks, high-page-count books, and materials that undergo frequent flexing. While EVA-based perfect binding can meet the strength requirements for many catalogs and magazines, its performance often diminishes on heavily coated or smooth papers unless factors like adhesive laydown, milling depth, and dwell time are carefully controlled.
Further research into structural and bookbinding adhesives highlights how even minor adjustments in polymer composition can significantly affect binding strength. For PUR systems, factors like curing conditions and isocyanate content are directly tied to improved peel and shear performance, especially on coated or laminated materials where both mechanical anchoring and chemical bonding are crucial. Advanced analysis techniques, such as force–displacement curves and energy-to-failure measurements, show that tougher adhesive formulations not only withstand higher loads but also absorb more energy before failing. This translates to better durability during repeated bending, opening, and handling, aligning with the goal of achieving consistent binding quality and enhancing overall print durability.
Industry Standards and Updated Protocols
To ensure consistency, updated industry protocols now provide clear standards for evaluating binding strength. For peel strength, ASTM D903 is widely used, while ASTM D1002 serves as the benchmark for lap-shear tests. Tensile and page-pull evaluations often adapt ASTM D882 guidelines, incorporating print-specific modifications for specimen preparation and normalization (e.g., force per inch of spine). These standards define key parameters such as test speeds, conditioning requirements, and data reporting formats.
Recent updates emphasize the importance of standardized conditioning, precise specimen preparation, and clearly defined acceptance criteria to minimize variability across laboratories. For example, using consistent crosshead speeds, fixed peel angles, and standardized fixture geometries has been shown to improve the reproducibility of adhesive bond tests. Newer protocols also mandate reporting additional metrics, such as failure modes and energy absorbed to failure, offering a more comprehensive understanding of binding performance. This approach addresses practical concerns, like pages loosening over time, with greater accuracy.
Round-robin studies involving multiple laboratories have further demonstrated the benefits of harmonized testing methods. These studies show that consistent procedures can significantly reduce variability, allowing multi-site printers and binderies across the United States to align their quality standards more effectively.
What is Peel Testing?
Mechanical vs. Computational Testing Methods
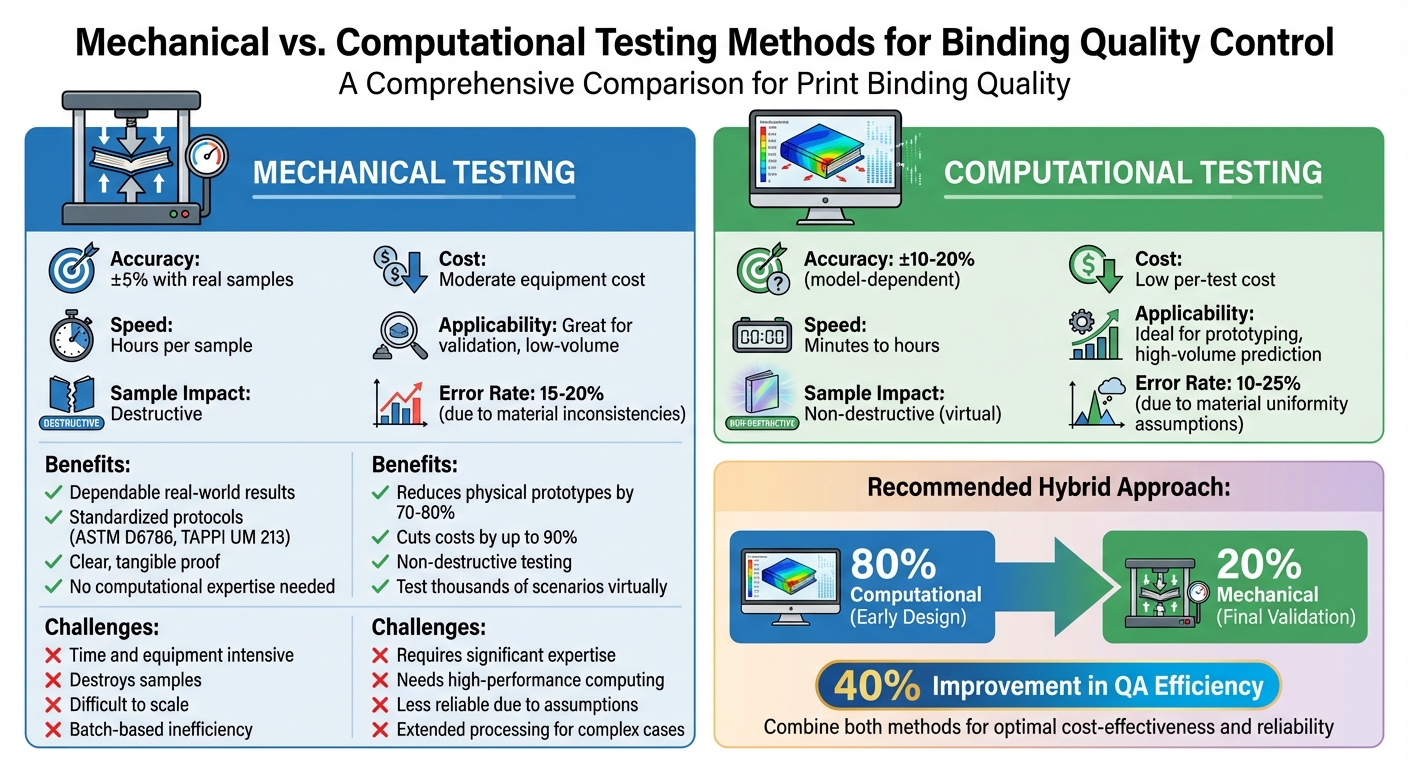
Mechanical vs Computational Binding Testing Methods Comparison
Understanding binding failure through both direct measurement and simulation is essential for ensuring print durability and performance.
Mechanical Testing: Benefits and Challenges
Mechanical testing delivers dependable results by directly measuring how materials fail under real-world conditions. Tools like universal testing machines operate under standardized protocols, such as ASTM D6786 for assessing book binding peel strength or TAPPI UM 213 for wire stitch pull tests. These tests are straightforward to perform and don’t require advanced computational expertise. Plus, they offer clear, tangible proof that a print product meets industry standards.
That said, mechanical testing isn’t without its drawbacks. It demands time and equipment, and since the process destroys the samples, they can’t be reused. Material inconsistencies, like uneven adhesive curing, can lead to errors ranging from 15–20%. For large-scale production, this batch-based method can be inefficient and difficult to scale.
Because of these limitations, many are exploring computational methods as an alternative for predicting binding performance.
Computational Models for Binding Prediction
Computational approaches, like finite element analysis (FEA), simulate how adhesives and substrates respond to stress. By factoring in material properties such as Young’s modulus and peel energy, these models can predict binding performance under various conditions. Software like ANSYS allows designers to test thousands of scenarios virtually – adjusting for variables like temperature (e.g., a standard 70°F), humidity, or adhesive thickness – while cutting physical prototype needs by 70–80%.
These models offer quicker turnaround times (hours instead of days) and can slash costs by up to 90% by reducing the need for physical testing. They’re also non-destructive, making them perfect for refining designs in custom printing projects. However, computational models have their own challenges. They can be less reliable due to assumptions about material uniformity, leading to errors between 10–25%. Additionally, setting up these simulations requires significant expertise and access to high-performance computing resources, which can extend processing times for complex cases.
Comparison Table: Mechanical vs. Computational Testing
Here’s a quick breakdown of the two methods:
| Aspect | Mechanical Testing | Computational Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | ±5% with real samples | ±10–20% (model-dependent) |
| Cost | Moderate equipment cost | Low per-test cost |
| Speed | Hours per sample | Minutes to hours |
| Applicability | Great for validation, low-volume | Ideal for prototyping, high-volume prediction |
| Sample Impact | Destructive | Non-destructive (virtual) |
A Balanced Approach
Experts suggest combining the strengths of both methods. Start with computational models for early design iterations – handling roughly 80% of the work – and then use mechanical tests for final validation and spot-checks (the remaining 20%). This hybrid strategy can improve quality assurance efficiency by around 40%, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and reliability for commercial printing applications.
sbb-itb-ce53437
Case Studies and Practical Applications
Binding Strength Tests in Print Production
Testing in real-world conditions confirms the reliability of binding methods. For example, a 2024 study conducted by a U.S. commercial printer evaluated 10,000 perfect-bound catalogs using tensile strength testers aligned with TAPPI T 543 standards. Initially, 8% of the catalogs experienced spine cracking. However, by fine-tuning the PUR adhesive to 4 gsm, failures dropped significantly to just 1.2%, while customer satisfaction rose by 15%. These findings paved the way for improved quality protocols in production workflows.
Peel tests conducted under ASTM D5174 standards also highlighted issues with weak EVA adhesives in perfect-bound books. Addressing these weaknesses reduced returns by 25% and ensured the books could endure over 10,000 flex cycles. Similarly, coil pull-out and crimp strength tests on plastic coil-bound manuals led to a switch to 1.5mm PET coils, increasing the manuals’ lifespan from 500 to 2,000 page turns in demanding industrial environments.
Updated standards have further refined these testing approaches. For instance, during production runs of educational books, inline testers achieved 95% compliance with durability benchmarks, effectively preventing 20% of potential warranty claims. These advancements directly support the goal of producing long-lasting, high-quality binding solutions.
Quality Assurance in Custom Printing Projects
Building on these testing successes, quality control processes for custom printing projects are reaching new heights. Miro Printing & Graphics Inc., based in Hackensack, NJ, offers a prime example. The company employs burst bind testers and adhesion pull gauges to ensure the durability of perfect and coil bindings for manuals and catalogs. Their meticulous approach targets durability of up to 15,000 cycles for custom projects.
Miro’s process includes 1,000-page flex tests on coil-bound proposals and post-press audits using digital force gauges. Thanks to these rigorous quality checks, the company achieves defect-free results in 95% of its jobs, slashing reprints by 40% and boosting customer satisfaction ratings to an impressive 4.9 out of 5. Even with a 15–20% variance in adhesion for custom PUR bindings due to variable paper stocks, controlled production conditions ensure 98% first-pass quality across a wide range of projects, from menus to detailed reports.
A 2025 Printing Industries of America survey, which analyzed over 500 projects, revealed that strength testing significantly enhances outcomes. Books subjected to stringent testing lasted through 12,000 openings, compared to just 8,000 for untested products. Additionally, satisfaction rates improved by 28%, with Net Promoter Scores climbing to 75, compared to 47 for projects without rigorous testing.
Conclusion: Improving Print Quality Through Binding Strength Testing
Binding strength testing has become a cornerstone for commercial printers aiming to produce durable, professional-grade products. Studies and real-world examples demonstrate that methods like page pull tests, flex cycles, and adhesive strength measurements can significantly cut down on defects, returns, and customer complaints. By incorporating quality checkpoints during pre-production and production, printers can identify weak bindings early, safeguarding their reputation and financial outcomes.
This shift from subjective evaluations to measurable standards represents a major advancement in print quality control. Today’s advanced equipment allows for precise force measurements and detailed data logging, enabling fine-tuning of variables such as adhesive temperature, clamp pressure, and spine preparation. For instance, earlier discussions highlighted how PUR adhesives outperform EVA adhesives on coated stocks, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right adhesive for specific applications.
For full-service providers like Miro Printing & Graphics Inc. in Hackensack, NJ, these testing methods translate into actionable quality assurance practices. By setting internal standards for different binding types – whether for perfect-bound catalogs, coil-bound manuals, or saddle-stitched booklets – and rigorously testing new substrates or formats, they can confidently recommend binding solutions that meet practical durability requirements. Their processes, designed to withstand up to 15,000 flex cycles, reflect a meticulous approach to quality, ensuring projects consistently exceed durability expectations.
The benefits of rigorous binding strength testing are clear: longer-lasting products, happier customers, and fewer reprints. As industry standards like ISO 16763 and ISO 19594 gain traction, printers who adopt these protocols will stand out as technical leaders. This not only supports premium pricing but also fosters lasting partnerships with clients across corporate, educational, and institutional sectors. These advancements underscore the ongoing effort to raise the bar for print production quality and durability.
FAQs
What are the main differences between PUR and EVA adhesives used in binding?
When comparing PUR (Polyurethane Reactive) adhesives with EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) adhesives for binding, the key distinctions come down to strength, flexibility, and how well they hold up under different conditions.
- PUR adhesives are known for forming strong, flexible bonds that stand up well to heat, moisture, and aging. This makes them a top choice for projects that demand durability and high-quality, long-lasting results.
- EVA adhesives, on the other hand, are more budget-friendly and simpler to work with. However, they don’t offer the same level of durability or resistance to environmental factors, which can limit their use in projects that require longevity or need to withstand tough conditions.
Each option has its place, depending on the specific needs of your project.
What are the differences between mechanical and computational methods for testing binding strength?
Mechanical testing methods are known for their precise measurements, as they directly assess binding strength using advanced equipment. The downside? They often take more time and demand significant resources. On the flip side, computational methods are quicker and resource-efficient, utilizing simulations and predictive models to estimate outcomes. That said, these models may occasionally fall short in accuracy due to inherent assumptions or constraints.
To strike the right balance between accuracy and efficiency, many experts suggest integrating both methods for binding strength testing. This combined approach leverages the strengths of each technique, ensuring reliable and timely results.
Why is following industry standards like ASTM crucial for binding strength testing?
Adopting established industry standards like ASTM is crucial for delivering reliable and consistent results in binding strength testing. These guidelines play a key role in maintaining the quality and durability of printed materials, minimizing the chances of problems such as binding failures.
Sticking to these standards also ensures that businesses meet client demands and regulatory expectations, enabling them to produce professional, high-quality products while strengthening customer confidence.
Related Blog Posts
- Top 6 Binding Methods for Professional Documents
- Paper Surface Texture Testing Methods
- How Binding Choices Impact Print Durability
- Perfect Binding Glue Types: What to Know
https://app.seobotai.com/banner/banner.js?id=693dffd7df12e5e3fea890dd